An exploration of accommodation provision for irregular migrants in the context of alternatives to detention
Written by Rositsa Atanasova (Advocacy Expert, Center for Legal Aid – Voice in Bulgaria)
In many national contexts the application of alternatives to detention (ATD) remains limited in practice, because detention is applied by default to foreign nationals who have lost the right of residence, and not as a measure of last resort. According to EU and international law, states must consider ATD before depriving people of their liberty. Yet too often we see an improper reversal of the burden of proof, whereby it is up to people in irregular situations to contest the presumption of detention by proving that they fulfil the requirements for the application of alternatives.
In Bulgaria, the experience of the Centre for Legal Aid – Voice in Bulgaria (CLA) is that there is almost no individualised assessment of the principles of necessity, reasonableness and proportionality, as required by European and international legal standards. Instead, authorities are only willing to consider ATD when an individual has met the conditions in the law for the implementation of alternatives through case management support. Frequently, this includes a requirement that suitable accommodation be available.
In order to better understand current accommodation options in the EU and Bulgaria, as well as their potential for expansion in the context of ATD, in late 2021 I carried out a study on options for irregular migrants. Here, I explain my conclusions as well as the implications when it comes to ATD for people in immigration detention.
Accommodation Options for Irregular Migrants in the EU
The study of accommodation options for irregular migrants, which I conducted for CLA with the support of our donor EPIM, consists of a mapping paper and an advocacy strategy. The mapping paper systematises current practice in the EU and advances a new conceptual framework for analysis of the link between ATD and accommodation. It is based on desk research and fills a gap in recent research on the accommodation of irregular migrants in the EU. The advocacy document, in turn, explores current practice in Bulgaria and contains an action plan for the short and mid-term in order to improve access to accommodation and expand the use of ATD. It draws on meetings with a range of stakeholders including government agencies and local authorities, NGOs, service providers and beneficiaries. The interviews provided information about the range of existing services, which was not available through desk research alone.
The range of accommodation options for irregular migrants in the European context can be mapped on a matrix (Table 1) in relation to the nature of the service provider and the nature of any potential partner. The axes represent a spectrum of accommodation provision, from state-run housing to private accommodation through NGO and denomination-run residential options. Such a model allows us to visualize dependency on an intermediary to access accommodation alternatives and how much of that service-provision is dominated by the state. In addition, the chart illustrates potential new areas for service-creation that might not yet exist. The matrix is ultimately also an instrument for measuring whether responses are mostly community-based or institutional.
Table 1 – Summary of accommodation options for irregular migrants across the EU
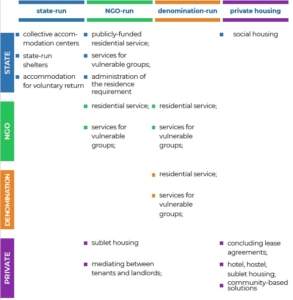 As illustrated by the examples above, accommodation for irregular migrants in the EU, if available at all, tends to be institutional and oriented towards return. In exceptional circumstances, people who cannot be deported to their country of origin can be accommodated in open reception centres for asylum-seekers or in homeless shelters. These options, however, are not presented as possible ATD, but as a way for authorities to provide a bare minimum of material assistance. The different housing possibilities presented here are most often used by irregular migrants who are not in contact with the authorities. Such pathways, however, can be quickly and usefully deployed to offer alternatives to detention in an emergency situation, as illustrated by regularisation initiatives during the pandemic. This is why it is useful to consider the full range of available choices in an effort to expand the ATD portfolio.
As illustrated by the examples above, accommodation for irregular migrants in the EU, if available at all, tends to be institutional and oriented towards return. In exceptional circumstances, people who cannot be deported to their country of origin can be accommodated in open reception centres for asylum-seekers or in homeless shelters. These options, however, are not presented as possible ATD, but as a way for authorities to provide a bare minimum of material assistance. The different housing possibilities presented here are most often used by irregular migrants who are not in contact with the authorities. Such pathways, however, can be quickly and usefully deployed to offer alternatives to detention in an emergency situation, as illustrated by regularisation initiatives during the pandemic. This is why it is useful to consider the full range of available choices in an effort to expand the ATD portfolio.
Accommodation Options for Irregular Migrants in Bulgaria
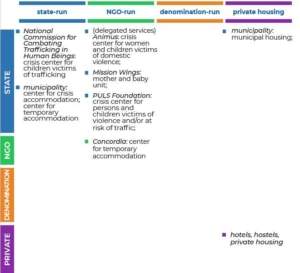
The study of accommodation options for irregular migrants in Bulgaria reveals a gradually shrinking space, however. Access to state services, State Agency for Refugees (SAR) reception centers and municipal housing have become more difficult to access even for beneficiaries of international protection, not to mention those in an irregular situation. Service providers are less willing to bend the rules to accommodate people without documents in crisis, particularly in light of pandemic measures. Mothers with children and victims of domestic violence or trafficking are the only groups that face fewer impediments, but even their access frequently involves protracted negotiations with service providers and social workers to renew referrals on a case by case basis. Placement in a service, ultimately, does not qualify as a formal ATD, but amounts to tolerated stay that is not formalized in any way.
Private housing remains the most readily available option for irregular migrants and the only one that currently qualifies as a formal ATD. The advantage of the Bulgarian system is that those who lend property to people without documents do not seem to incur criminal or administrative sanctions, in line with FRA recommendations. As a downside, private arrangements are onerous due to the need to find a guarantor who is willing to provide financial support, as well as to locate suitable accommodation amidst exploitative renting schemes, discrimination and limited choices.
Table 2 – Post-research mapping of housing options for irregular migrants in Bulgaria on the framework and template developed in the Mapping Paper
Implications for ATD
The results of the mapping and advocacy strategy, outlined above, demonstrate a wide variety of options when it comes to accommodation provision for migrants, including those that could be used within designated ATD initiatives. On the face of it, the Bulgarian accommodation requirement mentioned above could potentially be good news because it opens up the space for NGOs to develop accommodation options and case management programs for irregular migrants in order to expand the use of ATD for those at risk of immigration detention. Moreover, we know how essential stable and appropriate accommodation is for those going through migration processes; the government requirement could be seen as a recognition of this. By drawing on lessons learned across the EU, and developing additional accommodation models, the implication is that advocates for the rights and liberties of migrants can encourage a shift on the part of governments to using ATD.
The reality, however, is more complex. Given the standing presumption of detention in Bulgaria, it is not clear whether the availability of more housing options for irregular migrants will necessarily lead to greater application of alternatives. Instead, it seems that the accommodation requirement is being used as an excuse to justify the government’s failure to systematically consider ATD, linked to a general political resistance to community-based solutions (including on national security grounds).
CLA practice indicates that authorities tolerate stay in services when it will spare them the responsibility for vulnerable individuals and are more willing to apply ATD when presented with ready-made solutions. The implication, therefore, is that whilst accommodation remains a key part of ATD programmes, the provision of more accommodation options alone is unlikely to be the catalyst for change that it might seem at first glance to be. Provision of accommodation, whilst a key part of ATD, is certainly not a silver bullet. Instead, the reversal of the ATD logic – which sees detention as the primary precautionary measure, as opposed to a measure of last resort – should be challenged on its own terms. In particular, it is essential that the burden of proof is turned back around so that presumption of liberty, rather than detention, becomes the norm. In Bulgaria, possible routes lie in advocating for access to services on the basis of the new Law on Social Services, which is theoretically applicable to all persons within the jurisdiction, and NGOs stepping in as mediators, guarantors or service providers for irregular migrants.
Find out more about the work of Centre for Legal Aid – Voice in Bulgaria, including their pilot ATD programme, here.